Riding the Waves: Understanding Kondratieff Cycles and the Rhythm of Capitalist Economies.
Capitalist economies, far from progressing in a linear fashion, exhibit a fascinating pattern of long-term cycles. These cycles, known as Kondratieff Waves (or K-waves), offer a framework for understanding the ebb and flow of economic prosperity and economic depression.
The Genesis of Kondratieff Waves (K-Wycles)
Named after the Russian economist Nikolai Kondratieff, these waves describe long-term economic cycles, typically lasting 40 to 60 years.
Since the 18th century, economists have observed several Kondratieff Waves, each driven by major technological advancements:
1st | 1780-1830: The first wave, driven by the steam engine.
2nd | 1830-1880: The second wave, propelled by steel and railroads.
3rd | 1880-1930: The third wave, marked by electrification and chemical industry innovation.
4th | 1930-1970: The fourth wave, fueled by automobiles and petrochemicals.
5th | 1970-Present: The fifth wave, centered on information technology. Some economists posit the emergence of a sixth wave, driven by biotechnology and healthcare.
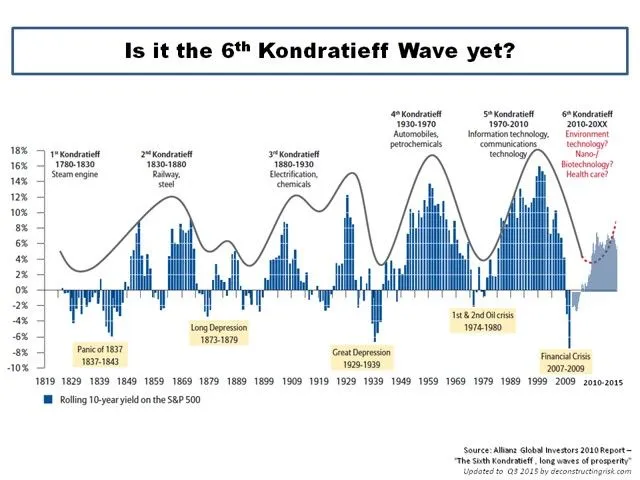
Kondratieff’s research, conducted in the early 20th century, revealed recurring patterns of boom and bust in capitalist economies, driven by major technological innovations.
Kondratieff Waves (K-Wycles)
Each Kondratieff Wave is characterized by distinct phases:
- Ascending Phase (Spring/Summer):
- This phase is marked by the emergence of groundbreaking technologies, leading to increased productivity, economic growth, and rising prosperity.
- New industries emerge, creating jobs and driving investment.
- This period is often associated with optimism and a sense of progress.
- Descending Phase (Autumn/Winter):
- As the initial wave of innovation matures, growth slows, and markets become saturated.
- Overcapacity, increased competition, and financial speculation can lead to economic downturns.
- This phase is characterized by periods of recession or depression, with rising unemployment and economic hardship.
The Role of Technological Innovation
A key driver of Kondratieff Waves is technological innovation.
Major breakthroughs, such as the steam engine, electricity, and information technology, have each triggered periods of rapid economic expansion.
These innovations create new industries, transform existing ones, and generate significant productivity gains.
However, the benefits of these innovations are not evenly distributed, and the transition to new technological paradigms can be disruptive.
Contemporary Relevance of Kondratieff Waves (K-Wycles)
Understanding Kondratieff Waves can provide valuable insights into the current economic landscape.
- Many economists believe that we are currently transitioning into a new K-wave, potentially driven by advancements in areas such as biotechnology, renewable energy, and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- It is important to understand that there are many differing oppinions on where in the wave we currently are, and if the wave theory is completely accurate.
- By recognizing the cyclical nature of capitalist economies, businesses and policymakers can better prepare for future challenges and opportunities.
Possible Future Kondratieff Waves
Predicting the future with absolute certainty is impossible, but based on current trends and analyses of Kondratieff Waves, several potential drivers for future waves have been identified. Here’s a breakdown of some prominent possibilities:
- Biotechnology and Healthcare. This is frequently cited as a strong contender. Advances in genomics, personalized medicine, and longevity research could revolutionize healthcare and create a massive economic impact. The aging global population and increasing focus on preventative care further fuel this potential wave.
- Green Technologies and Sustainable Energy. Climate change concerns are driving a global shift towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal. Innovations in energy storage, smart grids, and sustainable materials could form the basis of a new economic cycle.
- Artificial Intelligence and Robotics. Continued advancements in AI and robotics have the potential to automate numerous industries, leading to significant productivity gains and economic restructuring. This includes the development of advanced AI that can create new AI, and the advancement of robotics to the point of self replication.
- Space Exploration and Commercialization. The growing commercialization of space, including satellite internet, space tourism, and asteroid mining, could create new industries and economic opportunities.
- Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials. Developments in nanotechnology could lead to breakthroughs in materials science, with applications in various fields, from electronics to medicine.
Key Considerations about Future Kondratieff Waves
It’s important to remember that Kondratieff Wave theory is a subject of ongoing debate, and there’s no universal agreement on its validity.
The interplay between these technologies could also be a significant factor. For example, AI could accelerate advancements in biotechnology or green technologies.
Global events, such as pandemics, and geopolitical situations, can also have a large impact on the direction of economic trends.
In essence, future Kondratieff Waves are likely to be driven by technologies that fundamentally reshape our economy and society. Sources and related content
Summary
In summary, Kondratieff Waves highlight the long-term cyclical nature of capitalist economies. Technological innovation is a primary driver of these cycles. Understanding K-waves can help us anticipate future economic trends and prepare for periods of both prosperity and downturn.
While the precise timing and nature of future K-waves remain uncertain, the theory provides a valuable framework for analyzing the dynamic and evolving nature of the global economy.
 Articles: 1,400 · Readers: 740,000 · Views: 2,209,961
Articles: 1,400 · Readers: 740,000 · Views: 2,209,961 